东海高级中学2005—2006学年度第一学期高二第三次月考
英 语 试 题
范围: Units 6-8 BII 考试时间: 120分钟,共150分 命题人:刘恩县
第一卷(三部分,共115分)
第一部分:听力(共两节,满分30分)
第一节:(共5小题:每小题1.5分,满分7.5分)
听下面5段对话。每段对话后有一个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。听完每段对话后,你都有10秒钟的时间来回答有关小题和阅读下一小题。每段对话仅读一遍。
1. What time is it?
A. 8:00. B. 9:00. C. 10:00.
2. What is Peter going to do this afternoon?
A. Play basketball. B. Ride a bicycle. C. Go swimming.
3. How much is the woman going to pay?
A. 20 pence. B. 25 pence. C. 30 pence.
4. How will the man travel to New York?
A. By car. B. By train. C. By plane.
5. What is the woman doing?
A. Making a suggestion. B. Asking for help. C. Offering advice.
第二节:(共15小题:每题1.5分,满分22.5分)
听下面5段对话或独白,每段对话后或独白后有几个小题。从题中所给的A、B、C三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。听完每段对话或独白前,你将有时间阅读各个小题,每小题5秒钟;听完后,各小题将给出5秒钟的作答时间。每段对话读两遍。
听第6段对话,回答6至7题。
6. What does the man do?
A. He's an engineer. B. He's a salesman. C. He's a traveler.
7. What's the relationship between the two speakers?
A. They are friends.
B. They are strangers.
C. They are shop assistant and customer.
听第7段对话,回答8至9题。
8. What is the man looking for?
A. He's looking for a book.
B. He's looking for some paints.
C. He's looking for a colored pencil.
9. Where has the woman found it?
A. On the desk. B. In the comer under the desk. C. In the desk.
听第8段对话,回答10至12题。
10. Whom does the man want to talk with?
A. Mr. White. B. Jim. C. Mr. Smith.
11. Where is Dr. Smith?
A. He is in his office. B. Nobody knows. C. He went home.
12. Which number is correct?
A. . B. . C. .
听第9段对话,回答13至16题。
13. Where does this conversation take place?
A. At a bank. B. At an airport ticket office. C. At a police station.
14. Where was the woman’s money probably stolen?
A. It was probably in the bank.
B. It was probably in the moving stair from the underground.
C. It was probably outside the bank.
15. How much of her money was stolen?
A. £4,500. B. £5,400. C. £4,900.
16. What is the woman doing in the city?
A. She is on a business trip there.
B. She is a visitor there.
C. She is a citizen there.
听第10段独白,回答17至20题。
17. John's mother wasn't a German, was she?
A. No, she wasn't. B. Yes, she was. C. She may not be.
18. Which languages do John's parents both speak?
A. German, Polish and French.
B. German, French and Italian.
C. German, French and English.
19. When was John born?
A. Less than one year after their parents got married.
B. More than one year after their parents got married.
C. More than two years after their parents got married.
20. What other languages does John know besides English?
A. French and Polish. B. German and Italian. C. French and German.
第二部分:英语知识运用(共两节, 满分45分)
第一节:单项填空(共15小题,每小题1分,满分15分)
21. ______ the doctor really doubts is ______ the little boy will recover from the serious disease soon.
A. What, when B. What, whether C. That, how D. Which, if
22. ______ is a fact that English is being accepted as an international language.
A. There B. This C. That D. It
23. After you arrive in Shanghai, you might ______ in touch with a friend of mine.
A. get B. have C. make D. put
24. The man insisted ______ a taxi for me even though I told him I lived nearby.
A. find B. to find C. on finding D. in finding
25. I suffered a lot ______ smoking, so I gave ______ last year.
A. to, it up B. to, up it C. from, it up D. from, up it
26. Take your raincoat ______ rain.
A. in case B. in case of C. in case it D. in that case
27. She sent a postcard, ______ us every success.
A. hoping B. wishing C. expecting D. wishing for
28. The plant is dead. I ______ it more water.
A. will give B. would have given C. must give D. should have given
29. It was ordered that no smoking ______ in the library.
A. be allowed B. is allowed C. can be allowed D. allows
30. Since the ice cream is delicious, my friend recommended that it ______ by everyone here.
A. tasted B. should taste C. be tasted D. be tasting
31. I can’t become infected_______ HIV by swimming in a pool, or sitting in a bath.
A. to B. by C. with D. at
32. I'm sorry but I __________ that you __________ your homework.
A. don't notice, are doing B. don't notice, were doing
C. didn't notice, have done D. didn't notice, were doing
33. The town is no longer __________ it was five gears ago, it was quite dirty.
A. what, which B. that, which C. what, when D. that, where
34. I can’t stand him. He always talks as though he everything.
A. knew B. knows C. has known D. had known
35. We do out best to be careful and prevent bad things______, but most of us will eventually find ourselves in a situation_______ we or others need help.
A. from happening; which B. to be happened; where
C. happening; where D. to be happened; which
第二节 完型填空(共20小题;每小题1.5分,满分30分)
阅读下面短文,撑握其大意,然后从36—55各题所给的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出最佳选项
I Passed My Drive Test!
I’d been 16 for six days and was already prepared to deal with failure.
I remember that, when my mum 36 me that morning, her voice wasn’t as screaming as it usually was. She had been 37 for more than one hour getting everything ready, and I could feel she was 38 me at the same time.
I stayed in bed for a few minutes. I was 39 to leave its warmth and 40 and unwilling to face the suffering that I’d rather let myself forget for the past months. Finally, I dragged myself 41 .
The first thing I thought of after getting up was to 42 . I went to the kitchen and prepared a breakfast that was fairly 43 , but was still too big for my appetite(食欲,胃口) that day. I kept telling myself that I 44 eat. Breakfast is the most important meal of the day, and this wasn’t a(n) 45 day. Besides maybe it would 46 me a little. But I doubted it. I left the kitchen because even the 47 made me feel sick.
I finished getting ready and tried to settle down. It didn’t 48 , so I decided that my mum and I should go. We had 49 time, so I thought we could practise parking. I 50 , with the wheel hitting the pavement(人行道). After that, the little bit of confidence(自信) I had was 51 . I tried two more times, but did not improve much. Then we went towards the driving 52 site (地点).
I waited twenty minutes---just enough time to make myself believe that I was going to fail. Then, finally, it was my 53 . I wasn’t sure of myself at all. I just wanted to get it over and make sure that I had to come back next Thursday.
The first thing I had to do was parking, which I did quite well. The 54 that came with it hit me like a wave. The rest of the test went well and I passed it.
The 55 of my mum made her face softer. I knew her worry was gone and she was happy for me.
36. A. cried B. woke C. told D. shouted
37. A. up B. over C. out D. in
38. A. smiling at B. worrying about C. looking at D. talking with
39. A. sad B. eager C. unwilling D. willing
40. A. convenience B. friendship C. quiet D. comfort
41. A. out of bed B. onto bed C. into bed D. in bed
42. A. eat B. rest C. drink D. work
43. A. large B. small C. delicious D. good
44. A. might B. could C. should D. hated
45. A. important B. necessary C. lucky D. ordinary
46. A. calm B. hurt C. stop D. like
47. A. milk B. bread C. smoke D. smells
48. A. work B. do C. calm D. use
49. A. little B. plenty of C. no D. a little
50. A. cried B. succeeded C. failed D. left
51. A. back B. gone C. there D. greater
52. A. start B. office C. race D. test
53. A. try B. turn C. car D. chance
54. A. happiness B. pride C. confidence D. disappointment
55. A. tears B. lines C. smiles D. eyes
第三部分:阅读理解(共20小题,每题2分,满分40分)
阅读下列短文,从每题所给的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出最佳选项。
A
When I asked my daughter which item she would keep: the phone, the car, the cooker, the computer, the TV, or her boyfriend, she said “the phone”. Personally, I could do without the phone entirely, which makes me unusual, because the telephone is changing our lives more than any other piece of technology.
Point 1. The telephone creates the need to communicate, in the same way that more roads create more traffic. My daughter comes home from school at 4:00 pm and then spends an hour on the phone talking to the very people she has been at school with all day. If the phone did not exist, would she have anything to talk about?
Point 2. The mobile phone means that we are never alone. “The mobile saved my life,” says Crystal Johnstone. She had an accident in her Volvo on the A45 between Otley and Skipton. Trapped inside, she managed to make the call that brought the ambulance to her rescue.
Point 3. The mobile removes our secret. It allows marketing manager of Haba Deutsch, Carl Nicolaisen, to ring his sales staff all round the world at any time of day to ask where they are, where they are going, and how their last meeting went.
Point 4. The telephone separates us. Antonella Bramante in Rome says, “We worked in separate offices but I could see him through the window. It was easy to get his number. We were so near—but we didn’t meet for the first two weeks!”
Point 5. The telephone allows us to reach out beyond our own lives. Today we can talk to several complete strangers at one time on chat lines (at least my daughter does. I wouldn’t know what to talk about). We can talk across the world. We can even talk to astronauts (if you know any) while they’re space-walking. And, with the phone line hooked up to the computer, we can access the Internet, the biggest library on Earth.
56. How do you understand ‘Point 1—The telephone creates the need to communicate,…’?
A. People don’t communicate without telephone.
B. People communicate because of the creating of the telephone.
C. People communicate more since telephone has been created.
D. People communicate more because of more traffic.
57. Which of the following best shows people’s attitude towards mobile phones?
A. Mobile phones help people deal with the emergency.
B. Mobile phones bring convenience as well as little secret to people.
C. Mobile phones are so important and should be encouraged.
D. Mobile phones are part of people’s life.
58. Which points do you think support the idea that phones improve people’s life?
a. Point 1. b. Point2. c. Point3. d. Point 4. e. Point 5.
- c, d B. a, e C. a, c D. b, e
59. It is possible to talk to several complete strangers at one time through _____.
A. the TV screen B.
a fax machine
C. the phone line hooked up to the computer D.
a microphone
B
|
A border collie named Rico recognizes the names of about 200 objects, say researchers in Germany. The dog also appears to be able to learn new words as easily as a 3-year-old child. Its word-learning skills are as good as those of a parrot or chimpanzee(黑猩猩).
In one experiment, the researchers took all 200 items that Rico is supposed to know and divided them into 20 groups of 10 objects. Then the owner told the dog to go and fetch one of the items and bring it back. In four tests, Rico got 37 out of 40 commands right. As the dog couldn’t see anyone to get clues, the scientists believe Rico must understand the meanings of certain words.
In another experiment, the scientists took one toy that Rico had never seen before and put it in a room with seven toys whose names the dog already knew. The owner then told Rico to fetch the object, using a word the dog had never heard before.
The correct object was chosen in seven out of 10 tests, suggesting that the dog had worked out the answer by process of elimination(排除法). A month later, Rico remembered half of the new names, which is even more impressive.
Rico is thought to be smarter than the average dog. For one thing, Rico is a border collie, a breed(品种)known for its mental abilities. In addition, the 9-year-old dog has been trained to fetch toys by their names since the age of nine months.
It’s hard to know if all dogs understand at least some of the words we say. Even if they do, they can’t talk back. Still, it wouldn’t hurt to sweet-talk your dog every now and then. You might just get a big, wet kiss in return!
60. From paragraph 2 we know that .
A. animals are as clever as human beings
B. dogs are smarter than parrots and chimpanzees
C. chimpanzees have very good word-learning skills
D. dogs have similar learning abilities as 3-year-old children
61. Both experiments show that .
A. Rico is smart enough to get all commands right
B. Rico can recognize different things including toys
C. Rico has developed the ability of learning mathematics
D. Rico won’t forget the names of objects once recognizing them
62. Which of the following statements is true?
A. The purpose of the experiments is to show the border collie’s surprising mental abilities.
B. Rico has a better memory partly because of its proper early training.
C. The border collie is world-famous for recognizing objects.
D. Rico is born to understand its owner’s commands.
63. What does the writer want to tell us in this passage?
A. To train your dog. B. Dogs are good at learning new words.
C. To be careful with your dog. D. Some dogs might understand what we say.
C
An apple a day may poison children.
Children who eat an apple or pear a day may be beyond the pesticide(杀虫剂) safety limit because of the remains on the fruit, according to research.
Using data of the British Department of Environment on pesticides on fruit collected from supermarkets,scientists thought that each day some children would get a poisonous level of pesticides.
The research, published on Sunday, says the government repeatedly claims that the levels of pesticide are safe because,instead of measuring individual apples, researchers buy 10, crush them and take an average reading to see if they are safe. This is the internationally agreed method of checking remains.
But government figures show that the pesticide is not averagely spread across the batch(一批), and one or two apples could contain 90% or more of the pesticide in the batch.
It used mathematical modeling to measure exposure(暴露) to pesticides for children aged between 18 months and four years old. The pesticides involved can destroy children’s hormones and some are suspected(怀疑) of causing cancer.
The good news for British fruit growers is that samples grown in this country had lower residue level than imported fruit, so buying home-produced fruit will reduce the danger, said Emily Diamand,one of the Earth’s senior food researchers and one of the authors of the report.
64. The reason why “An apple a day may poison children” is that ______.
A. there are some pests in the apple
B. children would get a poisonous level of pesticides because of the remains on the apple
C. there are always more pesticides on the apples produced in Britain
D. the apple is too hard for children to eat
65. The internationally agreed method of checking remains is to buy ______.
A. two apples, crush them and take an average reading to see if they are safe
B. five apples, crush them and test to see if they are safe
C. ten apples, crush them and take an average reading to see if they are safe
D. eighty apples, and then test them by crushing
66. The underlined word “residue” can be replaced by ______.
A. remains B. pesticide C. quality D. medicine
67. Which of the following is NOT true?
A. The remains of the pesticides can do harm to the children’s health.
B. The remains of the pesticides can do harm to the children’s hormones.
C. Some remains of the pesticides are suspected of causing cancer.
D. For safety,we’d better not import apples from Britain.
D
International Studies(BA)
Key features
l Recognizes the “global community”
l Has close connections with practical research
l Much of the teaching is done in small discussion groups
About the course
The course gives you chances to know great power polities between nations .It will provide more space to study particular issues such as relationship among countries in the European Union, third world debt, local and international disagreement, and the work of such international bodies as the United nations ,the European Union, NATO, and the World Bank.
The course puts theories into the working of the international system with close attention to particular countries. You will also have a better knowledge of methods of solving the international problems.
Related courses
BA (Hons) Community Management
BA (Hons) Public Policy and Management
Employment possibilities
International organizations
International business
Earth Science (BSc)
Key features
l Based on key course and the latest research findings
l Pays much attention to practical skills
l Offers chances for fieldwork
About the course
The demand for natural resources is becoming an increasingly serious problem for the future of mankind. Graduates in Earth Science will play an important role in meeting this demand, and in knowing the meaning of using the natural resources.
The course covers geography and geology. You will carry out fieldwork in the UK and possibly overseas, and a research in an area of interest to you in the final year.
Related courses
BSc (Hons) Geography
BSc (Hons) Geology
Employment possibilities
Mineral, oil , water or other related engineering industries.
68 . After taking the course of International Studies, the students will ____.
A. become practical and open-minded B. have a greater ability to discuss theories
C. know how to settle international problems D. have good jobs in international organizations
69. Earth Science, as described in the second text, _____.
A. is attractive because of the chances for fieldwork
B. pays more attention to practical skills than theories
C. is built on important courses and the result of recent studies
D. encourages students to play a role in using natural resources
70 .It can be inferred that the above two texts are written for the students who _____.
A. enjoy research work B. plan to choose courses
C. study in the UK D. are interested in overseas fieldwork
E
After the violent earthquake that shook Los Angeles in 1994, earthquake scientists had good news to report: The damage and death toll(死亡人数)could have been much worse.
More than 60 people died in this earthquake. By comparison, an earthquake of similar intensity(强度)that shook America in 1988 claimed 25 000 victims.
Injuries and deaths were relatively less in Los Angeles because the quake occurred at 4:31 a.m. on a holiday, when traffic was light on the city’s highways. In addition, changes made to the construction codes in Los Angeles during the last 20 years have strengthened the city’s buildings and highways, making them more resistant to quakes(抗震).
Despite the good news, civil engineers aren’t resting on their successes. Pinned to their drawing boards are blueprints(蓝图)for improved quake-resistant buildings. The new designs should offer even greater security to cities where earthquakes often take place.
In the past, making structures quake-resistant meant firm yet flexible materials, such as steel and wood, which bend without breaking. Later, people tried to lift a building off its foundation, and insert rubber and steel between the building and its foundation to reduce the impact of ground vibrations. The most recent designs give buildings brains as well as concrete and steel supports. Called smart buildings, the structures respond like living organisms to an earthquake’s vibrations. When the ground shakes and the building tips forward, the computer would force the building to shift in the opposite direction.
The new smart structures could be very expensive to build. However, they would save many lives and would be less likely to be damaged during earthquakes.
71. One reason why the loss of lives in the Log Angeles earthquake was comparatively low is that_______.
A. new computers had been installed in the buildings
B. it occurred in the residential areas rather than on the highways
C. large numbers of Los Angeles residents had gone for a holiday
D. improvements had been made in the construction of buildings and highways
72. The function of the computer mentioned in the passage is to_______.
A. counterbalance(起平衡作用)an earthquake’s action on the building
B. predict(预测)the coming of an earthquake with accuracy
C. help strengthen the foundation of the building
D. measure the impact of an earthquake’s vibrations
73. The smart buildings discussed in the passage________.
A. would cause serious financial problems
B. would be worthwhile though expensive
C. would reduce the complexity of architectural design
D. can reduce the ground vibrations caused by earthquakes
74. It can be inferred from the passage that in minimizing(使……最小)the damage caused by earthquakes, attention should be focused on_______.
A. the increasing use of rubber and steel in capital construction
B. the development of flexible building materials
C. the reduction of the impact of ground vibrations
D. early forecasts of earthquakes
75. The author’s main purpose in writing the passage is to_________.
A. compare the consequences of the earthquakes that occurred in the U.S
B. encourage civil engineers to make more extensive use of computers
C. outline the history of the development of quake-resistant building materials
D. report new developments in constructing quake-resistant buildings
分部:__________ 姓名:____________________ 考号: _________________
…………………………..……………装 …订….线……………………………………………..
第二卷(共35分)
第四部分:写作(共两节,满分35分)
第一节 短文改错(共10小题;每小题1分,满分10分)
此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标有题号的每一行作出判断:如无错误,在该行右边的横线上画一个勾(√);如有错误(每行只有一个错误),则按下列情况改正:
该行多一个词:把多余的词用斜线(\)划掉,在该行右边横线上写出该词,并也用斜线(\)划掉。
该行缺一个词:在缺词处加一个漏词符号(∧),在该行右边横线上写出该加的词。
该行错一个词:在错的词下划一横线,在该行右边横线上写出改正后的词。
注意:原行没有错的不要改。Dear Ralph,
A strange thing was happened in our garden the 76. ___________
other day. I went out play with my dog for 77. ___________
a few minute, and noticed the dog barking (吠) 78. __________
at a big tree. Before I realized that it meant, it 79. __________
started to dig a hole at the base of the tree. 80. ___________
Suddenly a large rat rushed out the hole, ran across 81. __________
the garden and disappearing into some waste ground 82. ___________
behind the garden. Surprising at this unexpected 83. ___________
incident, the poor dog was too slowly to react. It ran 84. ___________
to the fence, but without some result. 85. ___________
第二节 书面表达(满分25分)
假如你准备参加《中国日报》组织的题为“Nothing Is Small”的中学生英语短文比赛。比赛要求简要描述下列三幅画的内容,并陈述你从画中悟出的道理。
参考生词:1. 道钉:rail spike 3. 管涌:tube fountain
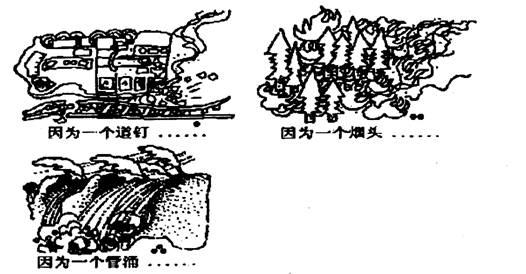
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
东海高级中学2005—2006学年度第一学期高二第三次月考
英 语 试 题 参 考 答 案
听力部分
1--5 CACBB 6-10 BAABC 11--15 CACBA 16--20 BCCBC
单选题:
21-25. BDACC 26-30. BBDAC 31-35. CDCAC
完型
36-40 BABCD 41-45 AABCD 46-50 ADABC 51-55 BDBCC
阅读理解
56-59 CBDC 60-63 CBBD 64-67 BCAD
68 C
69 C 根据第二部分第3行:Based on key course and the latest research findings
70 B 文章介绍了课程的features,related courses,及毕业后从业领域。
71 D 细节题。见文中第三段第二句话。
72 A 推测题。文中倒数第二段“当地面震动,建筑物倾斜时,电脑会使楼房向相反的方位移去”。
73 B 推断题。文中最后一段可推断此题的答案。
74 C 推断题。文中第三段告诉我们,在过去,要使建筑物防震就是意味着要用坚固又柔韧的材料。以后,人们又试图使建筑物抬高上升,在地基与房子间插入橡胶和钢材以减轻地面震动时的撞击。
75 D
短文改错
76. was happened---happened 77. play---- to play 78. minute----minutes
79. that----what 80. √ 81. out-----out of 82. disappearing----disappeared 83. Surprising-----Surprised 84. slowly----slow 85. some----any或去掉some
写作
Nothing Is Small
In our daily life, some great disasters frequently happen not because of something big but something small.
As are shown in the pictures, a train is turned over because a rail spike is loose without being fastened; a great forest fire breaks out because of live (burning) cigarette end (dog-end) thrown without being put out; a great dam is destroyed as a result of a tube fountain in a dam without being found out, which have all caused a great loss to both people and society.
We can learn, from the above examples, that nothing is small in our work and life and any behavior of carelessness or no responsibility or a small fault will result in great damage or disaster. So we should be very strict with ourselves and learn to be responsible and careful in our life and work.
