第一节 动词的时态
考试重点:一般现在时(if 从句和as soon as 从句);进行时表将来;现在完成时和现在完成进行时的区别;完成时瞬间动词以及have (has)been, have(has)gone的区别;过去完成时的时间状语;将来完成时。
一、一般现在式:
1、表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态:常和always, usually, often ,sometimes, every day, every week的等时间状语连用。
例:He goes to work every day. 他每天去上班。
2、表示普遍的真理。由于是众所周知的客观事实,所以一般不用时间状语。
例:The earth is round. 地球是圆的。
3、有些表示心理状态或感情的动词往往用一般现在时。
例:I don’t think you are right.我以为你错了。
4、在时间、条件状语从句中表示将来的动作:常用的连词有as soon as,when,till,if。
(1)They will go home for winter vocation as soon as they ________their exams.
A. have finished
B. finish
C. finished
D. was finishing
(答案:B)(1996年22题)
(2)When the mixture ______, it will give off a powerful force.
A. will heat
B. will be heated
C. is heated
D. has heated
(答案:C)(1992年59题)
二、一般过去时:
1、表示过去的动作或状态:常和过去时间状语连用。just now, last year, when I was 8years old等。
例:You've already missed too many classes this term .You _____ two classes just last week.
A. missed
B. would miss
C. had missed
D. have missed
(答案:A。有具体的时间状语要用过去时。)(1995年59题)
2、used to do sth:过去常常做…
例:I used to take a walk in the morning.
我过去是在早晨散步。(意味着现在不在早晨散步了。)
3、it is high time(that)…句型中,谓语动词用过去时。
例:Don’t you think it is time you _____ smoking?
A. give up
B. gave up
C. would give up
D. should give up
(答案:B)(1999年31题)
三、一般将来时
1、will(shall)+原形动词:表示将来的动作或状态。
例:He will come and help you. 他会来帮助你的。
2、be going to +动词原形:表示马上就要发生的事情或打算好要做的事。
例:Are you going to attend the lecture? 你打算去听这个演讲吗?
3、be to +动词原形: 表示安排或计划好了的动作。
例:The Third-Ring Road is to be open to traffic before National Day.
三环路将在国庆节前通车。
4、be about to +动词原形:表示即将发生的动作。
5、例:The lecture is about to begin.讲座即将开始。
6、某些表示开始、终结、往来行动的动词如:go ,come, start, arrive, leave 等的现在进行时可表示将来。
(1)We are leaving for Beijing tomorrow. 我们明天动身去北京。
(2)The foreign guests are arriving in Jinan tonight. 外宾今晚到达济南。
四、过去将来时
表示在过去预计将要发生的动作,常用于宾语从句。
例:He wanted to know when the conference would start.
他想知道会议何时开始。
五、现在进行时
1、表示此时此刻(说话时)正在进行的动作。
例:The teacher is talking with his students. 这位老师正在同他的学生交谈。
2、表示现阶段正在进行的动作,但此刻并不一定在进行。
例:I am attending a conference in Beijing. 我正在北京参加一个会议。
六、过去进行时
1、表示在过去某一段时间正在进行的动作。常需用表示过去的时间状语或通过上下文来判断时间。
例:He was doing his homework from seven to nine last night.
昨天晚上七点到九点他正在做作业。
2、when 和while 的用法
(1)I fell and hurt myself while I _____tennis.
A. was playing B. am playing C. play D. played
(答案:A。连接词when 表示时间上的点,其所引导的句子用过去时,while 表示持续的一段时间,其所引导的句子用过去进行时。)(1998年43题)
(2)When you _____ this over with her, you should not see her any more.
A. talk B. talked C. will talk D. talking
(答案为B)(1999年35题)
(3)One of the guards _____ when the general came in, which made him very angry.
A. has slept B. were sleeping C, slept D. was sleeping
(答案为D)(1996年23题)
3、过去进行时表示过去将来的动作。现在进行时可以表示将来的动作,同样,过去进行时也可以表示从过去某时间看将来要发生的动作。
例:He went to see Xiao Li. He was leaving early the next morning.
他去看小李。他第二天一早就要离开此地了。
七、现在完成时
1、表示动作刚刚结束(常和just, now, already, yet等词连用);或表示动作的结果(一般不用时间状语)。
(1)Li Ming has just turned off the light. 李明刚刚把灯关上。(说明现在灯已经关上了)
(2)I have lost my pen. 我把笔丢了。(说明过去某时丢的,现在我还没有找到这支笔。)
2、表示过去某时开始的动作一直延续到现在,并且可能会继续延续下去(常用since引导的短语或从句,或由for 引导的短语连用)。
(1)He has lived here for 30 years. 他住在这儿已经三十年了。(现在还住在这儿)
(2)They’ve known each other since childhood. 他们从小彼此相识。(现在还继续来往)
3、非延续性动词的完成时和it is +时间+since…..(过去时)
英语中有些动词不能延续, 因此不能和表示延续的时间状语连用。
(1)He has _____ the army for ten years and is now an officer.
A. gone into
B. joined in
C. been in
D. come into
(答案:C。用现在完成时表示“继续”的概念时,只能用含有持续意义的动词,不可用瞬间性动词。)(1995年49题)
(2)It is 3 years since I left Shanghai .我离开上海已经三年了。
(如果是非延续动词,这时常用 it is +时间+since 的句型代替,从句用过去时态。)
4、have(has)been to 和have (has)gone to 的区别
have(has )been to:去过某地(表示某人的一种经历),可以和once,twice,often,never,ever 连用。
have(has)gone to:去某地了(表示某人已经离开此地,在去某地的路途上或已在某地,所以一般来说此句型只用于第三人称),此句型不能与上述时间状语连用。
(1)He has gone to America.(意思为他已经去了美国,现在不在此地)
(2)He has been to America twice. 他去过美国两次。
八、过去完成时
1、表示在过去的某一时间或动作之前已经完成了的动作(即过去的过去)。这个过去的某一时间可用by, before等介词或连词引导的短语或一个从句来表示。
例:About the sixth century A.D. when few Europeans could read, the Chinese _____ paper.
A. invented
B. had invented
C. have invented
D. had been invented
(答案:B)(1997年35题)
2、表示从过去某一时间开始,一直持续到另一个过去的时间的动作。
例:The chemistry class _____ for five minutes when we hurried there.
A. had been on
B. was on
C. has been on
D. would be on
(答案:A)(1995年24题)
3、在含有before, after, as soon as 等连词引导的状语从句的复合句中,由于连词本身可以明确表示动作发生的先后顺序,因此,主句和从句都可以用一般过去时表示,而不用过去完成时。
例:I called him as soon as I arrived.我刚一到就给他打电话。
4、过去完成时常用在no sooner …than…, hardly/scarcely/barely…when…,一…就…。句型之中,句子到装。
(1)No sooner had we sat down _____ we found it was time to go.
A. than
B. when
C. as
D. while
(答案为A)(1997年50题)
(2)Scarcely had he opened the door when a gust of wind blew the candle out.
他刚打开门,蜡烛就被一阵风吹灭了。
九、将来完成时:表示在将来某一时间以前完成的动作。
1、By the time John gets home, his aunt _____.
A. will have
B. leaves
C. will have left
D. is leaving
(答案:C)(1995年25题)
2、I _____ writing the article by the time you get back.
A. shall finish
B. must have finished
C. have finished
D. shall have finished
(答案:D) (2000年24题)
十、现在完成进行时:表示从过去某时一直延续到现在的一个动作,这个动作一般会继续延续下去,或是到说话时结束, 但是强调到说话时为止一直在做的动作。
例:I _____ on the door for ten minutes now without an answer.
A. was knocking
B. am knocking
C. knocking
D. have been knocking
(答案:D)(1998年49题)
第二节 被动语态
考试重点:感官动词和使役动词的被动语态;动词短语的被动语态;情态动词的被动语态;用主动表示被动的含义。
一、感官动词及使役动词(如:see,feel,hear,watch,make,bid)在主动语态中用无to不定式做宾补,改为被动语态时要加to。
1、The middle-aged man was seen _____
out of the house on the afternoon of the murder.
A. came
B. come
C. to come
D. have come
(答案为C)(2000年58题)
2、We were made to study harder. 我们被要求努力学习。
二、有些动词后面接一个介词或副词,构成短语。变被动语态时,短语动词做及物动词用。
1、The children are well looked after. 这些孩子得到了很好的照顾。
2、The doctor has been sent for. 已经派人去请大夫了。
三、情态动词的被动语态
构成:情态动词+be+过去分词。
1、The work must be finished before
lunch. 这项工作必须在午饭前干完。
2、Nothing can be seen from here. 从这儿什么也看不见。
四、用主动表示被动的含义
常用:need/require +doing sth(=to be done)(此句型主语大多为物)
例:My room is a mess. It needs _____.
A to be tidying up
B. tidying up
C. to tidy up
D. tidied up
(答案为B)(2000年47题)
第三节 情态动词
考试重点:情态动词+完成时
情态动词用来表示能力、允许、许诺、可能、劝告、意愿等概念或态度。情态动词无人称变化,在句子中和动词原形一起构成谓语。根据这几年的考试看,着重测验情态动词接完成时的用法。
一、must +现在完成时
表示对已发生的事情的一种肯定的猜测。
1、Mr. Green _____ my letter, otherwise
he would have replied before now.
A. must have received
B. must have failed to receive
C. must receive
D. must fail to receive
(答案:B)(1998年44题)
2、I believe he _____ an accident,
otherwise he would have arrived on time.
A. would have had
B. could have had
C. should have had
D. must have had
(答案为D)(2001年58题)
二、should (ought
to )+完成时
表示应该做的事情而没有做,否定式表示不该做的事情做了。含有对过去的动作的责备、
批评。
1、They have done things they ought
_____.
A. not to do
B. not to be done
C. not to have done
D. not having done
(答案为C)(1999年59题)
2、I’m sorry I couldn’t get in touch
with him before he left, I _____ him earlier.
A. had a telephone
B. have phoned
C. should have phoned
D. should be phoned
(答案为C)(2000年26题)
三、could +完成时
表示能做的事情而没有做。表示对过去能做而未做的事情感到惋惜,遗憾。
1、He could have joined us, but he
didn’t get our invitation in time.
他本来能够参加我们的,但是他没有收到我们的请贴。
2、I could have passed, but I did not
study hard enough.
我本来能及格的,但是没有努力学习。
第四节 虚拟语气
如果所表示的条件根本不可能实现或实现的可能性很小时,称为虚拟条件句。
考试重点:虚拟语气的基本形式和用法;if的省略形式;含蓄条件句;以wish(that)引导的表示“愿望”的宾语从句;would rather 引导的从句;以as if, as though 引导的从句;以suggest,
advise, insist 等词后引导的宾语从句;It is necessary(important)that引导的主语从句;It is time (that)…句型中。
一、虚拟语气的基本形式和用法:
虚拟(条件)语气中,主句与从句中谓语动词的形式可分为下面三类:
1、I would ask George to lend us the money if I _____
him.
A. had known
B. have known
C. knew
D. know
(答案:C。与现在的事实相反,从句用过去时)(1995年38题)
2、Do you think there would be less
conflict in the world if all people _____ the same language?
A. spoke
B. speak
C. had spoken
D. will speak
(答案:A。与现在的事实相反,从句的谓语动词用过去时。)
3、If Bob____ with us, he would have
had a good time.
A. would come
B. would have come
C. had come
D. came
(答案为C。与过去的事实相反,从句的谓语动词用过去完成时。)(1995年59题)
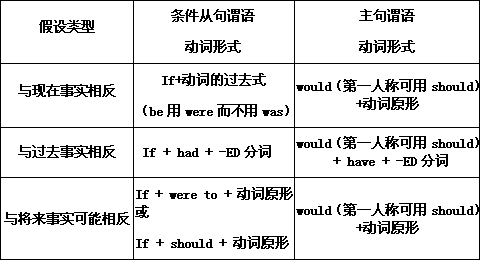
二、if的省略形式
在虚拟条件句中, 如谓语包含were , had, should等词, 则可以把这些词放到主语前面,省略if。
1、_____ you were busy, I
wouldn't have bothered you with my questions.
A. If I realized
B. Had I realized
C. Did I have realized
that
D. As I realized
(答案:B。虚拟条件句有时可以省略if,而将谓语中的过去式were,had,或should等移至主语之前。)(1996年39题)
2、_____, I should ask them
some questions.
A. Should they come to
us
B. If they come to us
C. Were they come to us
D. Had they come to us
(答案:A。与将来事实相反。)(1997年30题)
三、含蓄条件句
有时一个假设的情况不用条件从句表示,而用其它方式来表示,这样的句子叫含蓄条件句。常用with,without,but for。
1、Without your help, we
_____ so much.
A. didn’t achieve
B. would not have
achieved
C. will not achieve
D. don’t achieve
(答案:B。这是一句含蓄条件句,条件暗含在介词短语without your
help中,因此要用虚拟语气。)(1996年33题)
2、But for the rain, we
_____ a nice holiday.
A. should have
B. would have had
C. would have
D. will have had
(答案:B。2003年28题)
We could have done better under more favorable conditions.
假设我们有更有利的条件,我们还会做得更好。
But for his help,I should not have succeeded. 要是没有他的帮助,我就不会取得成功。
Without your help, we would not be able to finish the work in time.
要是没有你的帮助,我就不可能及时地完成工作。
But for his good education he would not have got the job.
要不是他受过良好的教育,他就不会得到这份工作。
With your aid I would have succeeded in performing my task.
当初若有你的帮助,我就会完成任务的。
He worked very hard; otherwise he might have failed. 他刻苦工作,不然他就失败了。
I would have written the paper before, but I have been ill.
我本来早就该写好这篇论文,但我一直在生病。
I would be most glad to help you, but I’m busy now.
四、以wish(that)引导的表示“愿望”的宾语从句
wish后的宾语从句中要用虚拟语气,而在虚拟语气中时态的应用类似在非真实条件中从句时态的应用。表示现在或将来的愿望用:主语+wish +从句(主语+过去时);表示一个过去没有实现的愿望用:主语+wish +从句(主语+过去完成时);
1、Peter wishes that he _____ law instead of literature when he was
in college.
A. could study
B. studied
C. had studied
D. would study
(答案:C)(2000年53题)
2、I didn’t go to the party, but I do wish I _____ there.
A. were
B. would be
C. had been
D. will be
(答案:C)(2001年53题)
1.主语+wish(that)+主语+did(be动词用were)+其他 宾语从句中用过去时
(be 用were的形式) 表示与目前的愿望相反。
She wishes she had more money. 她真希望有更多的钱。
I wish I were five years younger than you.我多么希望比你年轻五岁啊。
2. 主语+wish(that)+主语+ had done +其他 表示与过去的愿望相反。
I wish I had written to her. 我要是给他写信就好了。
I wished I had won the match.我要是打赢这场比赛就好了。
3. 主语+wish(that)+主语+ would/could +动词原形 +其他 表示将来不可能或未必可能实现的愿望。
I wish you would stay here longer. 我希望你在这儿多呆一会。
She wishes you wouldn't go. 她希望你不要走。
4. wish的时态不影响从句三种时间的判定。如果将wish 改为wished 其后that从句中的动词形式不变。
I wished I could help you. 我要是能帮助你就好了。
I wished I had written to her. 我要是给他写信就好了。
He wished that he were a teacher. 他真希望自己是个老师。
五、would rather+句子(过去时)
1、I’d _____ you didn’t
touch that, if you don’t mind.
A. rather
B. better
C. happier
D. further
(答为案:A)(1998年45题)
2、I am too busy these
days. I would rather all of you _____ next month for a dinner.
A. come
B. would come
C. came
D. have come
(答案为C)(2002年46题)
虚拟语气用于would rather 所跟的从句中,表示 “宁愿” “但愿”。从句动词用过去式表示当时或将来的情况,用过去完成式表示过去的情况。
| 主语+ would rather | (that) 虚拟语气从句 |
| I’d rather | you posted the letter right away. 我宁愿你马上就把这封信寄了。 |
| I would rather | that you hadn't told him.但愿你没有跟他讲过。 |
| I would rather | that you came tomorrow.我宁愿你明天来。 |
六、以as if,as though引导的从句
在as if,as though引导的从句中,如果谈论的是不可能或不真实的情况时,它们所引用的状语从句要用虚拟语气,动词形式和wish 后面的从中动词形式变化相同。
1、He talks as if he _____ everything in the world.
A. knows
B. knew
C. had known
D. would have known
(答案:B。as if(though)从句中非真实性情况用虚拟语气。本句表示说话人对现在的情况有所怀疑,所以用过去时。)
2、You are talking as if you had seen them
你谈的那么起劲,好像你真的见过似的。(表示想象中的过去的动作)
七、在表示要求、建议、命令等动词后的宾语从句中可以使用虚拟语气,其形式是“should +do”或省去should直接用动词原形(美国英语用法.)。这类should+动词原形型的虚拟语气,一般用于主语从句、宾语从句、表语和同位语从句中。它的使用主要取决于某些特定的表示要求、建议、命令的动词,名词和形容词。 这种类型的虚拟语气谓语由should+动词原形构成,无论什么人称都不能用 would,should在口语中可以略去。
句型说明:
1. 常用于这种句型的动词有: advise劝告 ask要求 command命令 decide决定
demand要求 desire 希望 determine 决心 insist坚持
intend 打算 move提议 order下令 prefer宁愿
promise 允诺 propose提议 recommend 推荐 request(请求)require要求 suggest建议 urge主张
有时,上述动词+宾语从句不是表示主张、建议或要求等,而是表示其它的意义,这时则仍用陈述语气。如当insist表示对已发生过的事物的看法,或当suggest为“说明了”,“暗示”等含义时,从句用直陈语气而不用虚拟语气。
He insisted that I was wrong. 他坚持认为我是错的。
The expression on her face suggests that she knows the secret.
她脸上的表情预示着她知道这个秘密。
2. 表示建议、要求、命令、假设等动词后面的宾语从句中,谓语用“should do”,should可省略。
They suggested (that) Tom go to see the doctor. 他们建议汤姆去看医生。
3. 在expect,believe, think, suspect等动词的否定或疑问形式后的宾语从句经常用“should+动词原形或完成形式)”,表示惊奇,怀疑,不满等。
I never expected that the problem should be so complicated. 我从没想到问题会这样复杂。
I just couldn’t believe that he should be so ignorant. 我简直不相信他会这样无知。
1、The doctor advised that
Mr. Malan _____ an operation right away so as to save his life.
A. had
B. would have
C. have
D. was going to have
(答案:C)(1998年28题)
2、His mother insisted that
he _____ the coat when going out.
A. put on
B. puts on
C. to put
D. putting on
(答案:A)(1999年58题)
八 虚拟语气在主语从句中表示惊奇、惋惜、理应如此等。带虚拟语气的主语从句主要有以下三种形式。
1. It is +形容词+ that 主语+(should)+动词原形 如:
It is natural that you should say apology to him.你自然应该向他道声歉。
这类形容词主要的有:
necessary (必须) essential (必要的), vital (极重要的,不可缺少的),
important (重要的) imperative(必须的),urgent(紧要的),advisable(应该的),
proper(适当的),obligatory (必须的),desirable(今人满意的,值得的),
appropriate(合适的),fitting (合适的), strange (奇怪), natural (自然的),
preferable (更好的),
1、It’s desired that she _____ to teach us at
least twice a week.
A. comes
B. will come
C. come
D. may come
(答案:C)(1997年29题)
2、It’s urgent that a meeting _____ before the final decision is
made.
A. will be arranged
B. must be arranged
C. be arranged
D. would be arranged
(答案:C)(2003年45题)
九、It is time (that)…引导的定语从句中,谓语动词用过去时。
1、It’s high time we _____ something to stop traffic accident.
A. do
B. will do
C. did
D. must do
(答案:C)(1996年43题)
2、Don’t you think it is time you _____ smoking?
A. give up
B. gave up
C. would give up
D. should give up
(答案:B)(1999年31题)
虚拟语气在目的状语从句中的运用)
| 主语+谓语….. | lest / for fear that / in case 主语+(should)+动词原形 |
| I wrote everything down | lest I (should) forget it. 我把每件事都记下来惟恐忘记了。 |
| Take your umbrella along | in case it (should) rain. 带着雨伞,以防下雨。 |
| He ran away | lest he (should) be seen. 他跑开了,以免被人看见。 |
| He doesn’t dare to go out | in case he should be recognized. 他不敢出去,以免被人认出来。 |
| She put a blanket over the baby | for fear that he should catch cold. |
第五节 非谓语动词
非谓语动词分三种,即:不定式,动名词和分词。下面分三部分进行介绍。
一、动词不定式
考试重点:动词不定式的基本结构和用法(尤其是复合结构,否定式,被动式,完成式等。);stop和go
on接不定式和动名词的区别;remember,forget接不定式和动名词的区别;have sth done 和have sb do sth。
基本形式
| 主动形式 | 被动形式 | |
| 一般式 | (not) to make | (not) to be made |
| 完成式 | (not) to have made | (not) to have been made |
| 进行式 | (not) to be making |
在句子中可以充当主语、宾语、表语、定语、状语和补足语。
(一)动词不定式的基本结构和用法
动词不定式是一种非谓语动词形式, 由不定式符号to加动词原形构成。
不定式作状语
1)目的状语
常用结构为to do , only to do(仅仅为了), in order to do, so as to do, so(such)… as to…(如此…以便…)。例如:
He ran so fast as to catch the first bus. 他飞快地跑以便赶上第一班车。
I come here only to say good-bye to you. 我来仅仅是向你告别。
2)作结果状语,可以表示没有预料到的或事与愿违的结果,不定式要放在句子后面。
I awoke to find my truck gone. 我醒来发现箱子不见了。
He searched the room only to find nothing. 他搜索了房间,没发现什么。
3) 表原因
I'm glad to see you. 见到你很高兴。
She wept to see the sight. 她一看到这情形就哭了。
4)表示理由和条件
He must be a fool to say so.
You will do well to speak more carefully.
1、Good-bye , Mr.
Wang. I’m pleased _____ you.
A. to meet
B .meeting
C. to have been
meeting
D. to be met
(答案:A)(1998年57题)
2、Encouragement
through praise is the most effective method of getting people _____ their best.
A. do
B. to do
C. doing
D. done
(答案为B)(1996年44题)
(二)动词不定式的被动式
当不定式的逻辑主语是不定式所表示的对象时(或动作的承受者时),不定式一般要用被动式。
1、The ability _____
is very important for any speaker.
A. to hear clearly
B. to be clearly
heard
C. to hearing
clearly
D. to being clearly
heard
(答案:B。动词不定式的被动式。)(1999年39题)
2、Mr. and Mrs. Smith
didn’t expect the house _____ so well.
A. to be decorated
B. to decorate
C. be decorated
D. decorating
(答案:A)(1995年22题)
三)动词不定式的复合结构
如需指出不定式动作的发出者时(即逻辑主语时)要在不定式前用for加名词(或代词)表示。
1、It was very difficult
_____ me to learn Spanish.
A. of
B. to
C. with
D. for
(答案:D)
注意: It's for sb.和 It's of sb.
这样的句子中,由于表语形容词性质的不同,导致了不定式逻辑主语标志用for或of的区别。
1)for sb. 句型中的形容词一般为表示事物的特征特点,表示客观形式的形容词,如easy, hard, difficult, interesting, impossible等:例如:
It's very hard for him to study two languages. 对他来说学两门外语是很难的。
2)of sb句型中的形容词一般为表示性格,品德,心智能力,表示主观感情或态度的形容词,如good, kind, nice, clever, foolish, right。例如:
It's very nice of you to help me. 你来帮助我,你真是太好了。
用for还是用of 的另一种辨别方法:
用介词for或of后面的逻辑主语作句子
2、It is necessary _____
the papers immediately.
A. for you to hand in
B. that you hand out
C. your hand in
D. for your hand in
(答案:A)
(四)动词不定式的完成式
表示不定式的动作发生在句子谓语所表示的动作之前。
1、Judging from his manners
at the party, he doesn’t seem _____ much education.
A. to receive
B. to be receiving
C. to have received
D. to have been received
(答案:C。表示发生在主要动词之前的动作,要用动词不定式的完成式。)(1997年45题)
2、The book is said _____
into several foreign languages up to now.
A. to translate
B. to have translate
C. to have been translated
D. to be translated
(答案:C)
特殊词精讲
forget doing/to do
forget to do 忘记要去做某事,forget doing 忘记做过某事。例如:
The light in the office is stil on. He forgot to turn it off. 办公室的灯还在亮着,他忘记关了。(没有做关灯的动作)
He forgot turning the light off. 他忘记他已经关了灯了。(已做过关灯的动作)
regret doing/to do
regret to do 对将要做的事遗憾,regret doing 对做过的事遗憾、后悔。例如:
I regret to have to do this, but I have no choice. 我很遗憾必须这样去做,我实在没有办法。
I don't regret telling her what I thought. 我不为告诉她我的想法而后悔。
cease doing/to do
cease to do 长时间,甚至永远停做某事,cease doing 短时停止做某事,以后还会接着做。例如:
That department has ceased to exist forever. 那个系已不复存在。
The girls ceased chatting for a moment when their teacher passed by. 姑娘们在老师走过时,停了会聊天。
try doing/to do
try to do 努力,企图做某事,try doing 试验,试着做某事。例如:
You must try to be more careful. 你可要多加小心。
I tried gardening but didn't succeed. 我试着种果木花卉,但未成功。
go on doing/to do
go on to do 做了一件事后,接着做另一件事,go on doing 继续做原来做的事。例如:
After he had finished his maths,he went on to do his physics. 做完数学后,他接着去做物理。
Go on doing the other exercise after you have finished this one. 作完这个练习后,接着做其他的练习
mean doing/to do
mean to do 打算、想,mean doing 意味着。例如:
I mean to go, but my father would not allow me to. 我想去,但是我父亲不肯让我去。
To raise wage means increasing purchasing power. 增加工资意味着增加购买力。
感官动词 + doing/ do
感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel + do表示动作的完整性,+doing 表示动作的进行性。例如:
I saw him work in the garden yesterday. 昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。(强调"我看见了"这个事实)
I saw him working in the garden yesterday.(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)昨天我见他正在花园里干活。
典型例题
1)They knew her very well. They had seen her ___ up from childhood.
A. grow B. grew C. was growing D. to grow
答案:A。因题意为,他们看着她长大,因此强调的是成长的过程,而非正在长的动作,因此用see sb do sth 的句型。
2)The missing boy was last seen ___ near the river.
A. playing B. to be playing C. play D. to play
答案A. 本题强调其动作,正在河边玩,应此用see sb. doing sth句型。
(五)stop 和go on后面接不定式和动名词的区别
动名词表示停下或继续正在做的事情;不定式表示停下以便做某事或改做另外一件事情。
1、The old man walked
slowly, stopping frequently _____.
A. on rest
B. at rest
C. resting
D. to rest
(答案:D。“to rest”作目的状语,意思为“停下来的目的是为了休息”。)(1999年29题)
2、Men will never stop
_____ for new ways of getting new energy.
A. search
B. to search
C. searching
D. searched
(答案:C)
3、You have been talking
for two hours. How long do you intend to go on _____ like that?
A. talking
B. to talk
C. doing talking
D. talk
(答案:A)
(六)remember 和forget接不定式和动名词的区别
remember, forget + doing
sth:表示动作发生在过去。
remember, forget +to do
sth:表示动作尚未发生。
1、Don’t forget _____ the
window before leaving the room.
A. to have closed
B. to close
C. having closed
D. closing
(答案:B。to close表示一个在leaving 之后发生的将来的动作)(2001年28题)
2、I remember giving the
letter to him.
我记得把信给他了。(giving表示一个在remember之前发生过的动作。)
(七)have sth done 和 have sb do sth的用法
1、We are going to have our
office _____ to make room for a new engineer.
A. to rearrange
B. rearrange
C. rearranged
D. rearranging
(答案:C。have sth done:表示这个动作由别人来做。)(2002年50题)
2、I’ll _____ that I’m a
qualified engineer.
A. have you know
B. have known you
C. have you knowing
D. have you known
(答案:A。表示让某人做某事。)(2003年25题)
I have my clothes ____ ,so I am busy.
A washed
B to be washed
C wash
D washing
I have my clothes washed, so I am free.
I
have my girlfriend wash my clothes
考试重点:动名词的逻辑主语,完成式,被动式,否定式;动名词做介词的宾语,有时介词可省略;“to”的作用。
基本形式:
| 主动形式 | 被动形式 | |
| 一般时 | doing | being done |
| 完成时 | having done | having been done |
在句子中可以充当主语、表语、宾语和定语。
动词可以用动名词作宾语。例如:
| admit 承认 | appreciate 感激 | avoid 避免 | complete完成 | consider认为 | delay 耽误 |
| deny 否认 | detest 讨厌 | endure 忍受 | enjoy 喜欢 | escape 逃脱 | fancy 想象 |
| finish 完成 | imagine 想象 | mind 介意 | miss 想念 | postpone推迟 | practice 训练 |
| recall 回忆 | resent 讨厌 | resume 继续 | resist 抵抗 | risk 冒险 | suggest 建议 |
| face 面对 | include 包括 | stand 忍受 | understand 理解 | forgive 宽恕 | keep 继续 |
| admit to | prefer…to | be used to | lead to | devote oneself to | object to |
| stick to | no good | no use | be fond of | look forward to | be proud of |
| be busy | can't help | be tired of | be capable of | be afraid of | think of |
| burst out | keep on | insist on | count on | set about |
|
| put off | be good at | take up | give up | be successful in |
|
to 可以用作介词,也可用作不定式的标示。下面的to 都用作介词:
| admit to | object to | be accustomed to | be used to | stick to | turn to开始 |
| look forward to | be devoted to | pay attention to | contribute to | apologize to | devote oneself to |
一、动名词的基本用法:
1、We shall appreciate _____ from you
soon.
A. being heard
B. hearing
C. to hear
D. having been heard
(答案:B。appreciate后接动名词做宾语。)(1998年42题)
2、John suggested _____ anything about
it until they found out more facts.
A. not to say
B. saying not
C. to say not
D. not saying
(答案:D。suggest后接动名词做宾语,否定式要在动名词前加“not”)(1995年53题)
二、动名词的完成时:表示的动作在谓语所表示的动作之前发生时,用动名词的完成时。
1、I don’t remember _____.
A. ever to be saying
B. to have ever said
C. having ever said that
D. ever said that
(答案:C)
2、I regret having done such a thing.我后悔做了这样的事。
三、动名词的被动式
1、No one avoid _____ by advertisements.
A. influenced
B. influencing
C. to influence
D. being influenced
(答案:D)
2、Susan was very unhappy for not _____ to the party.
A. to be invited
B. having been invited
C. inviting
D. to have been invited
(答案:B)
四、动名词的逻辑主语
当动名词的逻辑主语是代词时可使用形容词性的物主代词或代词的宾格。
1、He forgot about _____ him to attend my wife’s birthday party.
A. I asking
B. my asking
C. me to ask
D. mine to ask
(答案:B。做介词 about 的宾语, 物主代词+动名词,构成动名词的复合结构。)
(1998年29题)
2、I object to his (him)making private calls on the office phone.
我反对他用办公室的电话打私人电话。
五、动名词做介词的宾语,有时介词可省略。
1、Don’t risk _____ the job which so many people want.
A. losing
B. to lose
C. lost
D. your life to lose
(答案:A。risk后接动名词做宾语,risk(in)doing sth.中的介词in常省略。)
(1999年57题)
2、I don’t think it is any use _____ this matter any further.
A. discussing
B. to discuss
C. to discussing
D. to be discussed
(答案:A。it is no use (good)doing…做…没有用(好处),动名词做介词in的宾语,常省略。)
六、有的动词后的to 既可以是不定式符号,又可以是介词,使用时要特别注意。
1、You don’t object _____ you by your first name, do you?
A. for me to call
B. me to call
C. to my calling
D. my calling
(答案:C。object to 中的to是介词,故接动名词做宾语。)(1996年21题)
2、The students are looking forward to _____ their parents in winter
vacation.
A. see
B. watch
C. seeing
D. being seen
(答案:C)
worth 的用法
worth, worthy, worthwhile都是形容词,意为"值得"。
1). worth: be worth + n. 当名词为金钱时,表示"…… 值得……"
常见的有It ’s worth while to do./ It ’s worth(someone’s)while doing
be worth doing sth. "……某事值得被做"
The question is not worth discussing again and again. 这问题不值得反复讨论。
2). worthy:be worthy of +n. 当名词为抽象名词时表示"……值得……"
be worthy to be done "某事值得被做"
The question is not worthy to be discussed again and again.
3). worthwhile: be worthwhile to do sth "值得做某事"
It is worthwhile to ask him to join the club.值得邀请他加入俱乐
考试重点:分词在句中的作用;现在分词的被动式和过去分词的区别;现在分词和过去分词的区别;分词的逻辑主语与主句的主语是否一致;分词的独立主格;with(without)引导的分词的独立结构。
-ING分词是指由动词原形+-ING构成的、具有完成时态和被动语态的一种非谓语动词形式,具体形式如下:
| 主动形式 | 被动形式 | |
| 现在式 | doing | being done |
| 过去时 | Done | |
| 完成时 | having done | having been done |
就其语法功能而言,它可以作表语、补足语、状语和定语。
一、分词在句中的作用
1、She was sitting in an armchair _____
a book.
A. reading
B. to read
C. to be reading
D. to have read
(答案:A。分词短语在句中做伴随状语。)(1995年37题)
2、_____ anything about the accident,
he went to work as well.
A. Not know
B. Know not
C. Knowing not
D. Not knowing
( 答案:D。分词做原因状语)(2000年28题)
3、They all returned to the village
_____ that the danger was over.
A. convincing
B. convinced
C. to convince
D. having convinced
(答案:B。过去分词做伴随状语)(1997年57题)
4、We kept our _____ all night to
frighten the wolves.
A. burning fire
B. burnt fire
C fire burning
D. fire burnt
(答案:C。现在分词作宾补表示动作正在进行)(1997年55题)
二、现在分词和过去分词的区别
1、She told me that it was the most
_____ gift her daughter had received.
A. delighting
B. delighted
C. delights
D. delight
(答案:A。现在分词修饰的是事物,常译作“令人……”,具有主动、进行的意思。过去分词修饰人,常译作“感到……”,具有被动、完成的概念。又如:a moved audience:受感动的观众。)(2003年38题)
2、My parents are _____ with my
progress.
A. please
B. pleased
C. pleasing
D. being pleased
(答案:B。)
三、现在分词的被动式和过去分词的区别。
1、The interviewer should
take down notes at the moment the person _____ answers the questions.
A. to be interviewed
B. interviewing
C. being interviewed
D. interviewed
(答案:C。现在分词的被动式。表示动作正在发生)(1997年33题)
2、Standing on the bank,
the children watched the ship _____ with all kinds of goods.
A. loading
B. being loaded
C. to be loaded
D. having loaded
(答案:B。现在分词的被动式。)(2000年23题)
3、We found the eggs eaten
by the snake. 我们发现鸡蛋被蛇吃了。
(过去分词表示动作的完成和结果。)
四、分词的逻辑主语与主句的主语是否一致。
1、Arriving at the bus
stop, _____ waiting there.
A. he found a lot of
people
B. a lot of people were
C. he found a lot of
people’s
D. people were found
(答案:A。分词短语做伴随状语时,和主句共用一个主语。)(1996年37题)
2、_____ tired after a hard
work, she fell into bed and went straight to sleep.
A. Felt
B. Feeling
C. Being felt
D. To feel
(答案:B)(1998年50题)
分词作状语,可以表示时间,原因,理由,条件,让步,连续等,相当于一个状语从句。例如:
Not receiving any letter from him, I gave him a call. 由于没有收到他的信,我给他打了个电话。
As I didn't receive any letter from him, I gave him a call.
Given more attention,the trees could have grown better. 多给些照顾,那些树会长得更好。
If more attention was given, the trees could have grown better.
典型例题
1)_____ some officials, Napoleon inspected his army.
A. Followed B. Followed by C. Being followed D. Having been followed
答案B. Napoleon 与follow 之间有被动的含义。being followed除表达被动之外,还有动作正在进行之意。 followed by(被…跟随)。本题可改为: With some officials following, Napoleon inspected his army.
2)There was a terrible noise ___ the sudden burst of light.
A. followed B. following C. to be followed D. being followed
答案B. 由于声音在闪电后,因此为声跟随着光,声音为跟随的发出者,为主动。用现在分词。
3)_______, liquids can be changed into gases.
A. Heating B. To be heated C. Heated D. Heat
答案C. 本题要选分词作为状语。现在分词表主动,正在进行的;过去分词表被动的,已经完成的。对于液体来说是加热的受动者,是被动的,因而选C。它相当于一个状语从句 When it is heated,…
注意:选择现在分词还是过去分词,关键看主句的主语。如分词的动作是主句的主语发出,分词就选用现在分词,反之就用过去分词。例如:
Used for a long time, the book looks old. 由于用了很长时间,这本书看上去很旧。
Using the book, I find it useful. 在使用的过程中,我发现这本书很有用。
五、分词的独立主格:分词短语带有自己的逻辑主语,(一般由名词担任)称为分词的独立
主格。
1、The plane crashed, its
bombs _____ as it hit the ground.
A. exploded
B. were exploded
C. exploding
D. were exploding
(答案:C)(1999年43题)
2、Weather permitting,
we’ll go to the Summer Palace.
如果天气允许的话,我们去颐和园。
独立主格结构的特点:1)独立主格结构的逻辑主语与句子的主语不同,它独立存在。
2)名词或代词与后面的分词,形容词,副词,不定式,介词等是主谓关系。
3)独立主格结构一般有逗号与主句分开。
例如:
The test finished, we began our holiday. = When the test was finished, we began our holiday. 考试结束了,我们开始放假。
The president assassinated, the whole country was in deep sorrow. = After the president was assassinated, the whole country was in deep sorrow. 总统被谋杀了,举国上下沉浸在悲哀之中。
Weather permitting, we are going to visit you tomorrow. 天气允许,我们明天去看你。
This done, we went home. 工作完成后,我们才回家。
The meeting gone over, everyone tired to go home earlier. 会议结束后,每个人都想早点回家。
He came into the room, his ears red with cold. 他回到了房子里,耳朵冻得红通通的。
He came out of the library, a large book under his arm. 他夹着本厚书,走出了图书馆
六、with (without) 引导的分词的独立结构。
1、He walked across the
meeting room _____ everyone looking at her.
A. with
B. as
C. while
D. when
(答案:A。with或without可以引导分词的独立结构,做伴随状语。)(1997年49题)
2、With the old man _____
the way, we had no trouble in finding that mysterious cave.
A. leading
B. led
C. lead
D. to be led
(答案:A)(2000年27题)
with的复合结构作独立主格
表示伴随情况时,既可用分词的独立结构,也可用with的复合结构:with +名词(代词)+现在分词/过去分词/形容词/副词/不定式/介词短语。例如:
He stood there, his hand raised. = He stood there, with his hand raised.他举手着站在那儿。
典型例题
The murderer was brought in, with his hands ___ behind his back。
A. being tied B. having tied C. to be tied D. tied
答案D. with +名词(代词)+分词+介词短语结构。当分词表示伴随状况时,其主语常常用with来引导。由于本句中名词"手"与分词"绑"是被动关系,因此用过去分词,选D.
need/want/require/worth
当 need, want, require, be worth后面接doing时,表示的是被动意义。例如:
Your hair wants cutting. 你的头发该理了。
The floor requires washing. 地板需要冲洗。
典型例题
The library needs___, but it'll have to wait until Sunday.
A. cleaning B. be cleaned C. clean D. being cleaned
答案A. need (实意) +n /to do,need (情态)+ do,当为被动语态时,还可need + doing. 本题考最后一种用法,选A。如有to be cleaned 则也为正确答案
第六节 各种从句
英语中从句包括:名词从句、定语从句、同位语从句和状语从句。
一、名词从句包括主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句。
(一)主语从句
考试重点:主语从句常用的连词的用法;it is desirable that引导的主语从句的用法。
在句子中担当主语的是一个从句,这个从句就叫主语从句。主语从句可以由下列连词、连接代词和连接副词引导,且不能省略。
连词:that,whether
连接代词:what,whatever,who,whoever等。
连接副词:when,where,how,why
1、由连词that,whether引导的主语从句。
连词that,whether在主语从句中的作用只是引导主语从句,它在从句中不担任成分,不能省略,且由它们引导的主语从句,多用it做形式主语。
(1)_____ was unimportant.
A. Whether he enjoyed our dinner or not
B. No matter how he enjoyed our dinner
C. If he enjoyed our dinner
D. What he enjoyed our dinner
(答案:A)(2000年40题)
(2)That the earth is round is true.(It is true that the earth is round.)
地球是圆的, 是个事实。
2、由连接代词和连接副词引导的主语从句
它们分别在从句中担任主语、宾语和状语,不能省略。注意翻译时不能把它们译为疑问句。由它们引导的主语从句,也可以用形式主语it引导。
(1)Who let out the news remained
unknown.(It remained unknown who let out the
news.)
谁泄露了那个消息仍旧无人知道。
(2)When we’ll start is not clear.(It is not clear when we’ll start.)
我们何时出发还不清楚。
3、以关系代词what, whatever, whoever…引导的主语从句。
What有时可以用来表示the thing which这种意思,引导从句,表示一样东西或一件事情。Who,whom,which,what,可以和ever构成合成词,和what一样引导从句,ever起强调作用。此类句子不能用形式主语it引导,它们在句子中担任成份,不能省略,语序为陈述句的语序。
(1)_____ I saw was two men crossing the street.
A. What
B. Whom
C. Who
D. That
(答案:A)(2001年38题)
(2)_____ was not the way the event happened.
A. Which the press reported
B. That the press reported
C. what did the press report
D. What the press reported
(答案:D。主语从句,what在从句中做宾语。)(1998年24题)
4、句型It is desirable (suggested, necessary, requested, ordered, proposed, urgent)+that+主语+should(可省略)+V(动词原形)。
(1)It’s urgent that a meeting _____ before the final decision is
made.
A. will be arranged
B. must be arranged
C. be arranged
D. would be arranged
(答案:C)(2003年45题)
(2)It is highly desirable that a new president _____ for this
university.
A. is appointed
B. will be appointed
C. be appointed
D. has been appointed
(答案:C)(1997年52题)
虚拟语气在感叹句中的运用
If only引起的感叹句,也要求用虚拟语气。该结构中的动词形式与wish的宾语从句动词形式相同。与现在事实相反,谓语动词用过去式(be 一律用were);与将来事实相反,则用would/could+动词原形,与过去事实相反,则用had / could have +过去分词。
| If only | 主语 + 动词过去式 | |
| If only | he were still alive. 要是他还活着就好了。 | |
| If only | I were five years younger! 要是我能年轻5岁就好了! | |
| If only | she had never been married. 要是她从没有结婚就好了。 | |
二、定语从句
定语从句在句中做定语,修饰一个名词或代词,被修饰的名词词组或代词即先行词。定语从句通常出现在先行词之后,由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引出。
关系代词有:who, whom, whose, that, which等。
关系副词有:when, where, why等。
关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词所代替的先行词是人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。
1)who, whom, that
这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中作主语和宾语。例如:
Is he the man who/that wants to see you? 他就是你想见的人吗?(who/that在从句中作主语)
He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday. 他就是我昨天见的那个人。(whom/that在从句中作宾语)
2) whose 用来指人或物,(只用作定语, 若指物,它还可以同of which互换)。例如:
They rushed over to help the man whose car had broken down. 那人车坏了,大家都跑过去帮忙。
Please pass me the book whose (of which) cover is green. 请递给我那本绿皮的书。
3)which, that所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可作主语、宾语等。例如:
A prosperity which / that had never been seen before appears in the countryside.
农村出现了前所未有的繁荣。(which / that在句中作宾语)
The package (which / that)you are carrying is about to come unwrapped. 你拿的包快散了。(which / that在句中作宾语)
关系副词引导的定语从句
关系副词可代替的先行词是时间、地点或理由的名词,在从句中作状语。
1)关系副词when, where, why的含义相当于"介词+ which"结构,因此常常和"介词+ which"结构交替使用。例如:
There are occasions when (on which) one must yield. 任何人都有不得不屈服的时候。
Beijing is the place where(in which) I was born. 北京是我的出生地。
Is this the reason why (for which) he refused our offer? 这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗?
2)that代替关系副词,可以用于表示时间、地点、方式、理由的名词后取代when, where, why和"介词+ which"引导的定语从句,在口语中that常被省略。例如:
His father died the year (that / when / in which) he was born. 他父亲在他出生那年逝世了。
He is unlikely to find the place (that / where / in which) he lived forty years ago. 他不大可能找到他四十年前居住过的地方。
判断关系代词与关系副词
方法一: 用关系代词,还是关系副词完全取决于从句中的谓语动词。及物动词后面无宾语,就必须要求用关系代词;而不及物动词则要求用关系副词。例如:
This is the mountain village where I stayed last year. 这是我去年呆过的山村。
I'll never forget the days when I worked together with you.我永远不会忘记与你共事的日子。
判断改错:
(错) This is the mountain village where I visited last year.
(错) I will never forget the days when I spent in the countryside.
(对) This is the mountain village (which) I visited last year.
(对) I'll never forget the days (which) I spent in the countryside.
习惯上总把表地点或时间的名词与关系副词 where, when联系在一起。此两题错在关系词的误用上。
方法二: 准确判断先行词在定语从句中的成分(主、谓、宾、定、状),也能正确选择出关系代词/关系副词。
例1. Is this museum ___ you visited a few days age?
A. where B. that C. on which D. the one
例2. Is this the museum ____ the exhibition was held.
A. where B. that C. on which D. the one
答案:例1 D,例2 A
例1变为肯定句: This museum is ___ you visited a few days ago.
例2变为肯定句: This is the museum ___ the exhibition was held.
在句1中,所缺部分为宾语,而where, that, on which都不能起到宾语的作用,只有the one既做了主句的表语,又可做从句的宾语,可以省略关系代词,所以应选D。
而句2中, 主、谓、宾俱全,从句部分为句子的状语表地点,既可用副词where,又因 in the museum词组,可用介词in + which 引导地点状语。而此题中,介词on 用的不对,所以选A。
关系词的选择依据在从句中所做的成分,先行词在从句中做主、定、宾语时,选择关系代词(who, whom, that, which, whose); 先行词在从句中做状语时,应选择关系副词 ( where 地点状语,when 时间状语,why 原因状语) 。
限制性和非限制性定语从句
1) 定语从句有限制性和非限制性两种。限制性定语从句是先行词不可缺少的部分,去掉它主句意思往往不明确;非限制性定语从句是先行词的附加说明,去掉了也不会影响主句的意思,它与主句之间通常用逗号分开。例如:
This is the house which we bought last month. 这是我们上个月买的那幢房子。(限制性)
The house, which we bought last month, is very nice.这幢房子很漂亮,是我们上个月买的。(非限制性)
2) 当先行词是专有名词或物主代词和指示代词所修饰时,其后的定语从句通常是非限制性的。例如:
Charles Smith, who was my former teacher, retired last year. 查理·史密斯去年退休了,他曾经是我的老师。
My house, which I bought last year, has got a lovely garden. 我去年买的的那幢房子带着个漂亮的花园。
This novel, which I have read three times, is very touching. 这本小说很动人,我已经读了三遍。
3) 非限制性定语从句还能将整个主句作为先行词, 对其进行修饰, 这时从句谓语动词要用第三人称单数。例如:
He seems not to have grasped what I meant, which greatly upsets me. 他似乎没抓住我的意思,这使我心烦。
Liquid water changes to vapor, which is called evaporation. 液态水变为蒸汽,这就叫做蒸发。
说明:关系代词that和关系副词why不能引导非限制性定语从句。
as, which 非限定性定语从句
由as, which 引导的非限定性定语从句,as和which可代整个主句,相当于and this或and that。As一般放在句首,which在句中。例如:
As we know, smoking is harmful to one's health. 如我们所知,吸烟有害健康。
The sun heats the earth, which is very important to us. 太阳使地球暖起来,这对我们人类很重要。
典型例题
1)Alice received an invitation from her boss, ___came as a surprise.
A. it B. that C. which D. he
答案C. 此为非限定性从句,不能用 that修饰,而用which.,it 和he 都使后句成为句子,两个独立的句子不能单以逗号连接。况且选he句意不通。
2)The weather turned out to be very good, ___ was more than we could expect.
A. what B. which C. that D. it
答案B。which可代替句子,用于非限定性定语从句,而what不可。That 不能用于非限定性定语从句,it不为连词,使由逗号连接的两个句子并在一起在英语语法上行不通。
3)It rained hard yesterday, ____ prevented me from going to the park..
A. that B. which C. as D. it
答案B. as 和which在引导非限制性定语从句时,这两个关系代词都指主句所表达的整个意思,且在定语从句中都可以作主语和宾语。但不同之处主要有两点:
(1)as 引导的定语从句可置于句首,而which不可。
(2) as 代表前面的整个主句并在从句中作主语时,从句中的谓语必须是系动词;若为行为动词,则从句中的关系代词只能用which.。在本题中,prevent由于是行为动词,所以正确选项应为B。
as 的用法
例1. the same…as;such…as 中的as 是一种固定结构, 和……一样……。例如:
I have got into the same trouble as he (has). 我碰到了跟他一样的麻烦。
例2. as可引导非限制性从句,常带有'正如'。例如:
As we know, smoking is harmful to one's health. 如我们所知,吸烟有害健康。
As is known, smoking is harmful to one's health.
As是关系代词。例1中的as作know的宾语;例2中,它充当从句的主语,谓语动词know要用被动式。
关系代词that 的用法
1)不用that的情况
a) 引导非限定性定语从句时。例如:
(错)The tree, that is four hundred years old, is very famous here.
b) 介词后不能用。例如:
We depend on the land from which we get our food. 我们依赖土地获得食物。
We depend on the land that/which we get our food from.
2) 只能用that作为定语从句的关系代词的情况
a) 在there be 句型中,只用that,不用which。
b) 在不定代词,如:anything, nothing, the one, all, much, few, any, little等作先行词时,只用that,不用which。
c) 先行词有the only, the very修饰时,只用that。
d) 先行词为序数词、数词、形容词最高级时,只用that。.
e) 先行词既有人,又有物时。例如:
All that is needed is a supply of oil. 所需的只是供油问题。
Finally, the thief handed everything that he had stolen to the police. 那贼最终把偷的全部东西交给了警察。
考试重点:限定性定语从句中关系代词的用法;关系副词 when,where,why,引导的定语从句;带介词的定语从句;非限定性定语从句;“名词(代词)+介词+关系代词”引出,一般是非限定性定语从句。
在复合句中起定语作用的从句叫做定语从句。定语从句分为两种:限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句。注意关系代词和关系副词在从句中的应用。
(一)关系代词who,whom,whose,which,that引导的定语从句
1、The company official _____
I thought would be fired received a raise.
A. whom
B. whoever
C. who
D. of whom
(答案:A。关系代词whom在定语从句中做宾语,修饰先行词official)(1998年40题)
2、The investigation ,
_____ will soon be published, was made by John.
A. at which the results
B. the results on which
C. whose results
D. at whose results
(答案:C。关系代词whose 在定语从句中做定语。)(1998年58题)
(二)关系副词 when ,where, why, 引导的定语从句
1、The time will come _____
man can fly to outer space freely.
A. that
B. when
C. in that
D. which
(答案:B。when在定语从句中做状语。) (1996年35题)
2、I will never forget the
ten years _____ we both spent in the little village.
A. when
B. during which
C. which
D. in which
(答案:A)(2001年54题)
(三)关系代词前带介词的定语从句
1、Before her marriage, she
spent a considerable time in that very part of Shanghai, _____ she belonged.
A. which
B. to where
C. to which
D. at which
(答案:C。关系代词which和whom 还可以做“动词词组”后面的前置宾语。这里的动词词组是belong to。)(1998年56题)
2、The United States is
composed of fifty states, two of _____ are separated from the others by land or
water.
A. them
B. that
C. which
D. those
(答案:C)(2003年23题)
四)非限定定语从句对被修饰的名词起附加说明,或进一步描述或补充。
这种从句有一定的独立性,即使去掉,主句的意思仍然完整,只是内容相对地不够具体。与主句之间常用逗号分开,所用的关系代词与限定性定语从句基本相同,但不能用关系代词that 引导。
(1)An Old friend from
abroad, _____I was expecting to stay with, telephoned me from the airport.
A. that
B. whom
C. who
D. which
(答案:B)(2000年31题)
(2)His brother had become a
teacher, _____he wanted to be.
A. who
B. what
C. which
D. that
(答案:C。which引导的非限定性定语从句,在从句中做宾语,修饰先行词a teacher)(1997年39题)
(3)He has made another
wonderful discovery, _____of great importance to science.
A. which I think it is
B. of which I think it
is
C. I think which is
D. which I think is
(答案:D。which引导的非限定性定语从句,修饰前面整个句子。)(1995年50题)
(五)“名词(代词)+介词+关系代词”引出,一般是非限定性定语从句。
We’ve tested three
hundred types of boot, _____is completely water proof.
A. no of which
B. none of which
C. some of which
D. neither of which
(答案:B。“名词(代词)+of+which(whom)”引起的定语从句常表示部分与整体的关系。)(1995年36题)
状语从句
考试重点:状语从句的种类及一些连词的基本用法;让步状语从句;unless,supposed (that),whomever,whenever,wherever等连词的含义和用法。
在主从句中起状语作用的从句叫状语从句。常见的状语从句有时间、地点、条件、原因、让步、方式、比较、目的、结果。
一、时间状语从句
常用的连词有:when,whenever(无论什么时候),since,as,until,hardly…when,no sooner…than,as soon as,before,after,the moment,the minute(一…就…)
1、No sooner had they got
the goods covered up _____ it started raining hard.
A. when
B. than
C. then
D. after
(答案:B。no sooner…than 引导的时间状语从句。)(2002年57题)
2、She has wanted to become
a nurse _____ since she was a young girl.
A. long
B. often
C. always
D. ever
(答案:D。时间状语从句,ever since表示从…以后一直。)(1997年56题)
注意:如果hardly, scarcely 或no sooner置于句首,句子必须用倒装结构。例如:
Hardly / Scarcely had I got home when it began to rain.
No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
二、条件状语从句
常用if,unless(除非,如果不),as/so long as只要。
1、_____ I’m mistaken, I’ve
seen that man before.
A. Unless
B. If
C. Because
D. Provided
(答案:A。unless引导条件状语从句)(2001年40题)
2、_____ you return those
books to the library immediately you will have to pay a fine.
A. Until
B. Unless
C. If
D. Provided
(答案:B)(1998年60题)
三、原因状语从句
常用:because, as, since。如果表示必然的因果关系,一般用because引入;而since表示一种间接或附带的原因;用as 只是提一下。
1、He cannot go to school
because he is ill. 他因为生病不能上学。
2、Everyone likes you as
you are both kind and honest. 人人都喜欢你,因为你既和气,又诚实。
四、让步状语从句
常用though/although,as (尽管),even if/though,however,whatever,wherever,whoever,no matter how/what/who等。
1、In short, _____ he
lives, a man belongs to some society.
A. whatever
B. whenever
C. whichever
D. wherever
(答案:D。wherever引导让步状语从句,wherever = no matter
where)(1997年44题)
2、_____, you must show
your ticket to go into the cinema.
A. No matter whoever you
are
B. Whomever you are
C. Whoever you are
D. No matter who are you
(答案:C。whoever,引导让步状语从句,= no matter who)(1997年59题)
3、_____ you disagree with
her, her idea is still worth considering.
A. Even if
B. If only
C. Instead of
D. Despite of
(答案:A。让步状语从句。)(1998年44题)
4、Young _____ he is, he
knows what is the right thing to do.
A. that
B. as
C. although
D. however
(答案:B。as引导让步状语从句,被强调的部分放在句子之前,进行倒装。)
(2000年44题)
as, though 引导的让步从句必须表语或状语提前(形容词、副词、分词、实义动词提前)。例如:
Child as /though he was, he knew what was the right thing to do. 虽然是个小孩,该做什么不做什么,他全知道。
as / though引导的让步从句必须将表语或状语提前(形容词, 副词, 分词, 实义动词提前)。但需注意:
1) 句首名词不能带任何冠词。
2) 句首是实义动词, 其他助动词放在主语后。如果实义动词有宾语和状语,随实义动词一起放在主语之前。例如:
Try hard as he will, he never seems able to do the work satisfactorily. 他工作很努力,但总不能让人满意。
注意:让步状语从句中,有though,although时,后面的主句不能有but,但是 though 和yet可连用。
五、方式状语从句
常用as, just as, as
if/though 等词。
1、_____ was pointed above,
this substance can be used as a substitute.
A. It
B. That
C. What
D. As
(答案:D。As引导方式状语从句。)(1999年32题)
2、He talks as if he _____
everything in the world.
A. knows
B. knew
C. had known
D. would have known
(答案:B。as if(though)引导的方式状语从句,谓语动词用虚拟语气。)
六、目的状语从句
常用so that , in order that,
lest (以免, 以防), in case。
1、I wrote it down _____ I
should forget it.
A. in case
B. in case of
C. in order that
D. for fear of
(答案:A)(2002年27题)
2、I’ll give you my phone
number, so that you can call me when you arrive here.
我把我的电话号码告诉你,以便你到达这里后可以给我打电话。
七、结果状语从句
常用so…that, such…that
They are _____ students
that they all performed well in the nationwide examinations.
A. so diligent
B. such diligent
C. so much diligent
D. such very diligent
(答案:B)(2002年43题)
考试重点:形式上复数、意义单数的名词做主语;动名词、不定式,从句做主语;a number+of+复数名词和the number+of+可数或不可数名词做主语;主语由as well as 等词修饰时的主谓一致;当用and连接的名词前有each,every等修饰时,谓语动词用单数。
一、名词physics (物理),maths(数学),news(新闻),means(方法),works(工厂)等一般被认为是形式是复数,意思是单数的名词,它们做主语的时候动词一般用单数形式。
![]()
(答案:C。应改为is。)(2000年63题)
2、Every means has been tried. 每一种方式都试过了。
二、动名词、不定式、从句做主语时,谓语动词用单数。
When and where the new hospital will be built _____
a mystery.
A. to remain
B. remains
C. remain
D. is remaining
(答案:B)(2000年57题)
三、当主语是a number+of+复数名词时,谓语动词用复数;当主语是the number+of+可数或不可数名词时,谓语动词用单数
![]()
(答案:A。应改为the。1998年66题)
2、A number of cars _____ in front of
my house.
A. was parked
B. were parking
C. is parking
D. are parked
(答案:D)
四、当主语由as well as 等词修饰时的主谓一致。当句中的主语后接as well as,along
with,together with,including,accompanied
by等短语+名词(代词)时,主语与谓语的一致关系不受影响,主语是单数名词时,谓语动词用单数形式,主语是复数形式时,谓语动词用复数。
1、John, along with twenty friends, is
planning a party.
约翰和二十个朋友正在计划举行一个集会。
2、No one but Jane and Tom was there
then.
那时除了珍尼和汤姆之外,没有别人在那儿。
五、当用and连接的名词前有each,every等修饰时,谓语动词用单数。当主语是each…and…,every…and every…,many
a…and…结构时,谓语动词用单数。
1、Many a singer and dancer is to
attend our evening party.
许多歌唱家和舞蹈家将参加我们的晚会。
2、In our country every boy and every
girl has the right to receive education.
在我们国家每个人都有接受教育的权利。
第八节 倒装句
考试重点:
1、否定词放置句首时,助动词或be动词要放置主语的前面进行倒装。常用的否定词有:not,scarcely,barely,seldom,not until,little,(in)under no circumstance,by no means,no
sooner…than等。
句首为否定或半否定的词语,如no, not, never, seldom, little, hardly, at no time, in no way, not until… 等。例如:
Never have I seen such a performance. 从未见过如此糟糕的表演。
Nowhere will you find the answer to this question. 无论如何你不会找到这个问题的答案的。
Not until the child fell asleep did the mother leave the room. 母亲一直到孩子入睡后离开房间。
当Not until引出主从复合句,主句倒装,从句不倒装。注意: 如否定词不在句首不倒装。例如:
I have never seen such a performance.
The mother didn't leave the room until the child fell asleep.
典型例题
1) Why can't I smoke here?
At no time___ in the meeting-room
A. is smoking permitted B. smoking is permitted
C. smoking is it permitted D. does smoking permit
答案A. 这是一个倒装问题。当否定词语置于句首以表示强调时,其句中的主谓须用倒装结构。这些否定词包括no, little, hardly, seldom, never, not only, not until等。本题的正常语序是 Smoking is permitted in the meeting-room at no time.
2) Not until the early years of the 19th century ___ what heat is.
A. man did know B. man know C. didn't man know D. did man know
答案D. 看到Not until…的句型,我们知道为一倒装句,答案在C,D 中选一个。
改写为正常语序为,Man did not know what heat is until the early years of the 19th. 现在将not提前,后面就不能再用否定了,否则意思就变了
以否定词开头作部分倒装
如 Not only…but also, Hardly/Scarcely…when, No sooner… than等,要倒装。例如:
Not only did he refuse the gift, he also severely criticized the sender. 他没有收下礼物,还狠狠批评了送礼的人。
Hardly had she gone out when a student came to visit her. 她刚出门,就有个学生来访。
No sooner had she gone out than a student came to visit her. 她刚出门,就有个学生来访。
典型例题
No sooner___ than it began to rain heavily.
A. the game began B. has the game begun
C. did the game begin D. had the game begun
答案D. 以具有否定意义的副词放在句首时,一般采用倒装句(谓语前置)。这类表示否定意义的词有never, seldom, scarcely, little, few, not, hardly, 以及not only…but (also), no sooner…than, hardly… when scarcely… when 等等。
注意:只有当Not only… but also连接两个分句时,才在第一个分句用倒装结构。如果置于句首的Not only… but also仅连接两个并列词语,不可用倒装结构,如Not only you but also I am fond of music。
2、only+adv.句子要倒装。
Only in this way, can you learn English well. 只有这样,你才能学好英语。
Only after being asked three times did he come to the meeting. 叫了三次,他才来参加会议。
如果句子为主从复合句,则主句倒装,从句不倒装。例如:
Only when he is seriously ill does he ever stay in bed. 病得狠重时,他才卧床休息。
3、nor,neither,so用于句首时,句子要倒装。
用这些词表示"也"、"也不" 的句子要部分倒装。例如:
Tom can speak French. So can Jack. 汤姆会讲法语,杰克也会。
If you won't go, neither will I.你不去,我也不去。
典型例题
---Do you know Jim quarrelled with his brother?
---I don't know, _____.
A. nor don't I care B. nor do I care C. I don't care neither D. I don't care also
答案:B. nor为增补意思"也不关心",因此句子应倒装。A错在用 don't 再次否定,C neither 用法不对且缺乏连词。D缺乏连词。
注意:当so引出的句子用以对上文内容加以证实或肯定时,不可用倒装结构。意为"的确如此"。例如:
Tom asked me to go to play football and so I did. 汤姆邀我去踢球,我去了。
---It's raining hard.---So it is. 雨下得真大。是呀。
4、虚拟条件句中省略if时要倒装。
一、否定词放置句首时,助动词或be动词要放置主语的前面进行倒装。常用的否定词有:not,scarcely,barely,seldom,not until,little,(in)under no circumstance,by no means,no
sooner…than等。
1、Not until I reminded him for the
third time _____ working and looked up。
A. that he stopped
B. does he stopped
C. did he stop
D. that he stopped
(答案:C)(2000年53题)
2、_____ the importance of wearing seat
belts while driving.
A. Little they realize
B. They little do realize
C. Little realize do they
D. Little do they realize
(答案:D)(1996年31题)
二、only+ adv. 句子要倒装。
1、Only under such a condition will he
make steady progress.
只有在这样的条件下,他才会取得扎实的进步。
2、Only this morning did I hear the sad
news.
我今天早晨才听到这不幸的消息。
三、nor, neither, so 用于句首时,
句子要倒装。
1、So little _____about stock exchange
that the lecture was completely beyond me.
A. did I know
B. I had known
C. I knew
D. was I know
(答案:A)(1998年30题)
2、I didn’t finish reading that French
book, neither _____.
A. did he
B. didn’t he
C. he did
D. he could
(答案:A)
四、虚拟条件句中省略if时要倒装。
1、_____ you were busy, I wouldn’t have
bothered you with my questions.
A. If I realized
B. Had I realized
C. Did I have realized that
D. As I realized
(答案:B)(1996年39题)
2、_____, I should ask them some
questions.
A. Should they come to us
B. If they come to us
C. Were they come to us
D. Had they come to us
(答案:A)(1997年30题)
第九节 强调结构
考试重点:强调句型的基本形式It is(was)+被强调部分+that(who)…;强调句型用来强调状语。
一、强调句型的基本形式It is(was)+被强调部分+that(who)…。
![]()
(答案:B。应改为“that”)(1998年68题)
![]()
(答案:B。应改为who)
二、强调句型用来强调状语。
1、It was in that small room_____ they
worked hard and dreamed of better days to come.
A. where
B. in which
C. which
d. that
(答案:D。强调地点状语)(1997年58题)
2、It is because she is very devoted to
her students _______she is respected by them.
A. that
B. which
C. what
D. who
(答案:A。强调原因状语)(2001年33题)
3、It was not until she arrived in
class _________realized she had forgotten her book.
A. and she
B. when
C. she
D. that she
(答案:D)
常用的强调句结构是it 引导的句子,结构为It is(was)+ 被强调部分+ that (who) + 句子的其余部分。此结构强调的成分限于主语,宾语和状语。例如:
It is from the sun that we get light and heat. 我们是从太阳那儿获取光和热。
It was not until I had read your letter that I understood the true state of affairs. 知道读了你的信,我才知道实际情形。
典型例题
1)It was last night ___ I see the comet.
A. the time B. when C. that D. which
答案C. 强调句的结构是: It +be +强调部分 + that (who))+ 主谓句。 强调句的连词只有两个,that和who。当强调的部分是人,且为句子的主语时,才用 "who",其余用that。再如:原句:My father did the experiment in the lab yesterday evening.
2)It is ten years ___ Miss Green returned to Canada.
A. that B. when C. since D. as
答案C. 考点是连词用法。本题易误选为A. that. 其实本句不是强调句。若是,去掉It be… that还应是一个完整的句子。而本句去掉 'It is…that',只剩下ten years Miss Green returned to Canada. 不成句。因此本句不是强调句。
第十节 附加疑问句
考试重点:附加疑问句的基本用法;含有否定词的疑问句;祈使句的附加疑问句;一些特殊用法。
一、附加疑问句的基本用法
附加疑问句由两部分构成:陈述句+附加问句。一般的规则是:前肯定,后否定;前否定,后肯定。
1、He had to finish the work yesterday,
_____?
A. hadn’t he
B. had he
C. didn’t he
D. did he
(答案:C。have作“有”以外解释时,附加疑问句要用助动词do/does/did。)
2、There won’t be any concert this
Saturday evening _____?
A. will there not
B. will there
C. is there
D. will it be
(答案:B。当陈述句为there be句型时,附加疑问句用其否定或肯定的疑问句式。)
二、含有否定词的用法
若陈述句部分已有表示否定的 hardly,scarcely,never,seldom 等词时,反问句部分要用肯定。
1、She scarcely cares for anything
_____?
A. doesn’t
B. does she
C. is she
D. isn't she
(答案:B)(1995年45题)
2、You never told me you have seen the
film, _____?
A. had you
B. didn’t you
C. did you
D. weren’t you
(答案:C)(2002年53题)
三、祈使句:
1、Please let us have more time ,
_____?
A. shall we
B. will you
C. won’t you
D. don't you
(答案:B。Let’s表示第一人称的祈使句,反问部分主语用we时,谓语用shall。如:Let’s
go,shall we?)(1997年23题)
2、Don't forget to write to me, _____?
A. do you
B. won’t you
C. are
D. will you
(答案:D)(1994年37题)
四、一些特殊用法:
1、I suppose you’re not serious, _____?
A. don’t I
B. do I
C. are you
D. aren’t you
(答案:C。主句的谓语是suppose和think,主语是第一人称,反问句部分要和从句的谓语一致。)(1996年57题)再如 :“I don’t suppose you’re going today,
aren’t you?”
2、I don’t think you’ve heard of him
before, _____?
A. don’t I
B. do I
C. have you
D. haven’t you
(答案:C)(1992年33题)
第三章 答题技巧
第三节 挑错
挑错部分由10个单句组成,每个句子中有四个划线部分,其中有一个划线部分含有词汇或语法方面的错误,考生对错误挑出即可,不用改正,这一部分实际上是词语用法和语法结构部分的延伸,目的是测试学生掌握词汇、短语及语法结构的熟练程度, 重点固定搭配和句型。考试范围与第二部分相同。和其它三种题型相比较,它和词汇和语法结构部分一样,是相对比较简单的部分,考生应当在这一部分多得一些分数。常见错误类型分析:
一、用词错误
(一)固定搭配的错误
英语中固定搭配主要包括动词、形容词、名词同介词的搭配以及许多惯用法等。
![]()
(答案为A。neither…nor…既不…也不…,是固定搭配。)(2002年62题)
![]()
(答案为D。be forced to do sth:被迫做…,要接不定式。因此应改为to give up。)
(2002年64题)
(二)代词、替代词的错误

(答案为C。应改为our, 代指前面的those of us。)(2000年70题)
![]()
(答案为D。 应改为his,名词性的物住代词。)(2001年63题)
(三)连接词的错误
![]()
(答案为C。 应改为:what。what
引导宾语从句在句中做介词about 的宾语。)
(2002年65题)

(答案为B。应改为: two of which。非限定性定语从句,which在从句中指fifty
states。)(2000年62题)
二、语法错误
句型与语法结构方面的错误是另一类常见错误。主要体现在以下几个方面:
(一)主谓一致方面的问题,主要表现为数的不一致。
![]()
(答案为B。a good pair of glasses做主语, 动词要用单数。因此应改为was。)
(2001年69题)
![]()
(答案为C。应改为is。news
形式上是复数, 意思上是单数。)(2000年63题)
(二)语态和时态方面的问题
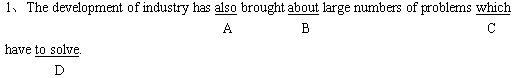
(答案为D。应改为:to be solved。因为solve 和他它的逻辑主语之间是动宾关系。再如:Nothing is allowed to be taken out of the building.任何东西都不能拿出这坐大楼。)
(2002年63题)
![]()
(答案为C。应该为 have had difficulty 。因为ever since 引导句子的时候,从句用过去时,主句要用现在完成时)(2001年62题)
(三)平行结构的错误
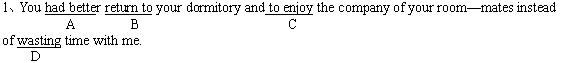
(答案为C。应改为:enjoy。因为enjoy 和return 并列,都跟在had better 后面,要用动词的原形)。(2001年70题)
![]()
(答案为C。应改为slammed, 因为句中, went out 和slammed
并列。)
(2001年65题)
(四)倒装方面的错误
![]()
(答案为B, 应改为shall we。1996年68题)
(五)虚拟语气方面的错误
![]()
(此句中C是错的,虚拟语气在这里的正确用法应当是go或者should
go。)
(1999年68题)
(六)肯定与否定的某些不定代词的用法

3.
(此句中C是错的。现在的双重否定变成肯定了。前半句还在夸历史学教授知识渊博,到了后半句突然变得不学无术了。nothing应改成anything。)(1998年69题)